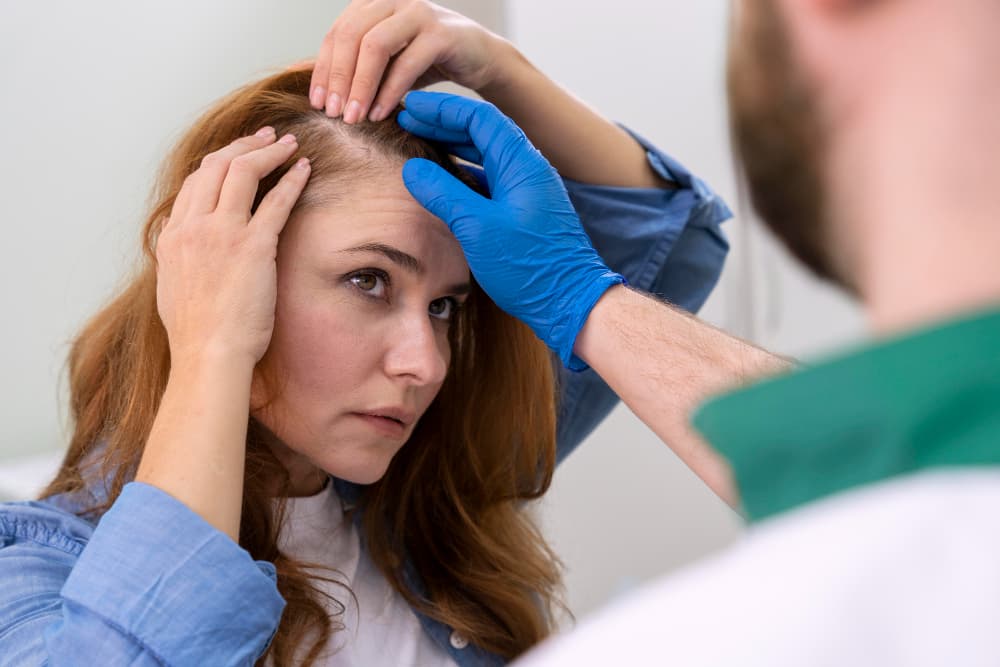
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA) is a distressing form of hair loss primarily affecting postmenopausal women, though men can also be afflicted. Characterized by a symmetrical band of hair loss along the front and sides of the scalp, FFA is a variant of lichen planopilaris—a condition that causes inflammation and scarring of the hair follicles.
This scarring can permanently damage the follicles, preventing new hair growth. Understanding the triggers and effective treatments is crucial for managing symptoms and potentially restoring hair growth, offering hope to those struggling with this challenging condition.
What is Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA)?
Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a chronic dermatological condition marked by progressive, symmetrical hair loss at the frontal hairline, eyebrows, and occasionally other parts of the body where hair grows. This form of alopecia is classified as a cicatricial or scarring alopecia because it involves inflammation that leads to the destruction of hair follicles and replacement with scar tissue. The hallmark of FFA is a smooth, band-like frontal recession of the hairline, which can vary in width and is often accompanied by a pale, shiny skin appearance in the affected area.
Identifying the Types of FFA
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is primarily observed in two distinct groups:
- Postmenopausal FFA: This is the most common type, typically affecting women in their postmenopausal years. The hormonal changes associated with menopause are thought to play a significant role in its development.
- Lichen Planopilaris-Type FFA: As a variant of lichen planopilaris, FFA shares some characteristics with this broader group of inflammatory hair disorders. In lichen planopilaris, the inflammation is not limited to the frontal scalp and can affect other parts of the scalp as well.
Understanding the Prevalence and Impact of FFA
Symptoms and Signs of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia

Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia manifests distinct symptoms that set it apart from other types of hair loss. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Recognizing the Progressive Hair Loss Pattern in FFA
The most noticeable symptom of FFA is a progressive thinning and recession of the hairline, primarily at the front and sides of the scalp. This recession typically presents as a symmetrical band of hair loss, and over time, it can extend to other areas like the eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair. The progression may be slow, often over several years, and can eventually stabilize on its own.
Identifying Other Associated Symptoms like Itching, Redness, and Scarring
In addition to hair loss, individuals with FFA may experience various inflammatory symptoms. These include:
- Itching: A common early symptom that may precede visible hair loss.
- Redness: The skin around the hairline may appear red and inflamed due to the underlying condition.
- Scarring: As the condition progresses, the affected areas often exhibit scarring where the hair follicles have been irreversibly damaged and replaced with fibrous tissue. The skin in these areas may appear smooth, pale, and devoid of hair follicles.
Differentiating FFA from Other Types of Hair Loss
Distinguishing FFA from other forms of alopecia is essential for appropriate management. Unlike androgenetic alopecia, which causes diffuse thinning without inflammation, frontal fibrosing alopecia involves a specific pattern of hairline recession accompanied by signs of skin inflammation and scarring.
It differs from non-scarring alopecias, where the hair follicles remain intact and hair regrowth is still possible. FFA’s similarity to other scarring alopecias, particularly lichen planopilaris, necessitates careful examination and sometimes biopsy to confirm the diagnosis and differentiate it effectively from other conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia

Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is influenced by a combination of factors, including autoimmune responses, hormonal changes, genetic predisposition, and external triggers. Understanding these factors can aid in better management and potentially in preventive strategies.
Exploring the Potential Autoimmune and Hormonal Factors
FFA is widely believed to have an autoimmune component, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy hair follicles, causing inflammation and subsequent scarring. This autoimmune reaction is central to the development of the condition. Additionally, hormonal factors are considered crucial, especially considering the high prevalence of FFA in postmenopausal women. Fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly a decrease in estrogen, are thought to contribute to its onset and progression.
Understanding the Role of Genetics and Family History
While the exact genetic mechanisms are not fully understood, genetics appears to play a role in FFA. A family history of similar hair loss patterns or other autoimmune conditions might increase an individual’s risk of developing FFA. Research is ongoing to identify specific genes involved, which could help in understanding the condition better and developing targeted treatments.
Identifying Other Contributing Factors like Stress and Medications
Other factors can exacerbate or trigger the onset of FFA. Stress is a well-known trigger for various autoimmune disorders and might also play a role in frontal fibrosing alopecia by affecting the immune system and hormonal balance. Additionally, certain medications have been associated with triggering or worsening the condition. These include some drugs used for treating cardiovascular diseases and hormonal therapies. It’s essential for patients and healthcare providers to review any potential drug-related risks and manage them accordingly.
Understanding these causes and risk factors allows healthcare providers to create more personalized treatment plans and offers insights into potential preventive measures for those at risk.
Diagnosis and Evaluation of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia

Proper diagnosis and evaluation of Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia are crucial for determining the most effective treatment strategies and managing the condition effectively. Here’s how healthcare professionals approach the diagnosis:
Importance of a Thorough Consultation and Physical Examination
The initial step in diagnosing FFA involves a thorough consultation and physical examination. During the consultation, the dermatologist will inquire about the patient’s medical history, family history of similar conditions, and any recent changes in health or lifestyle that could influence hair health. The physical examination focuses on the hair and scalp, assessing the pattern and extent of hair loss, the presence of scarring, and any signs of inflammation.
Utilizing Scalp Biopsies and Trichoscopy for Diagnosis
For a definitive diagnosis, further diagnostic tools are often utilized:
- Scalp Biopsy: This is a critical diagnostic tool in cases of FFA. A small section of scalp tissue, usually from the affected area, is removed and examined under a microscope. This helps to confirm the presence of inflammation and scarring typical of FFA.
- Trichoscopy: This non-invasive technique involves using a handheld device (dermatoscope) to magnify the scalp and hair follicles. It allows the dermatologist to observe the characteristic features, such as perifollicular erythema (redness around hair follicles) and loss of follicular openings.
Ruling Out Other Potential Causes of Hair Loss
To ensure accurate diagnosis, it is essential to rule out other causes of hair loss that might mimic frontal fibrosing alopecia . These include other forms of cicatricial alopecia, such as lichen planopilaris, and non-scarring alopecias like androgenetic alopecia or telogen effluvium. Comprehensive testing, which may include hormonal assays, blood tests to check for underlying autoimmune diseases, and a detailed review of the patient’s medication history, is often necessary to exclude these other conditions.
Treatment Options for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia

Managing Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia effectively requires a comprehensive treatment approach that focuses on halting the progression of hair loss, managing symptoms, and restoring hair appearance where possible. Here’s an overview of the current treatment strategies:
Understanding the Goals of FFA Treatment
The primary goals of treating frontal fibrosing alopecia are to stop the progression of the disease, alleviate any associated symptoms such as itching or inflammation, and improve cosmetic appearance. As FFA can lead to permanent hair loss due to follicle scarring, early intervention is crucial. Treatments are also aimed at maintaining the health of unaffected follicles and managing patient expectations regarding outcomes.
Exploring Topical Medications like Minoxidil and Finasteride
Topical medications are commonly used in the early stages of FFA:
- Minoxidil: Originally used for treating high blood pressure, topical forms of minoxidil can help in slowing hair loss and promoting hair regrowth in some patients by enhancing follicle size and prolonging the growth phase of hair cycles.
- Topical Finasteride: Unlike its oral form commonly used for male pattern baldness, topical finasteride can be used to decrease local DHT levels (a hormone linked to hair loss) without significant systemic effects, potentially slowing the progression of frontal fibrosing alopecia .
Considering Systemic Medications like Spironolactone and Dutasteride
In cases where topical treatments are insufficient, systemic medications may be considered:
- Spironolactone: This medication is an anti-androgen that helps in reducing the production of and sensitivity to androgens, which can exacerbate hair loss. It is particularly useful in female patients.
- Dutasteride: Similar to finasteride, dutasteride inhibits the conversion of testosterone to DHT but is more potent and inhibits more types of the enzyme involved. It’s used in cases resistant to other treatments.
Evaluating Hair Transplant Procedures for Advanced Cases
For patients with advanced hair loss where significant scarring and hair loss have occurred, hair transplant procedures might be considered as a last resort to restore the hairline aesthetically. This involves transferring hair follicles from denser areas of the scalp to the affected areas. However, it’s crucial to ensure that FFA is inactive as transplanting in active FFA can lead to the failure of the grafts due to ongoing inflammation.
When Hair Loss Is Permanent: Hair Transplant for FFA
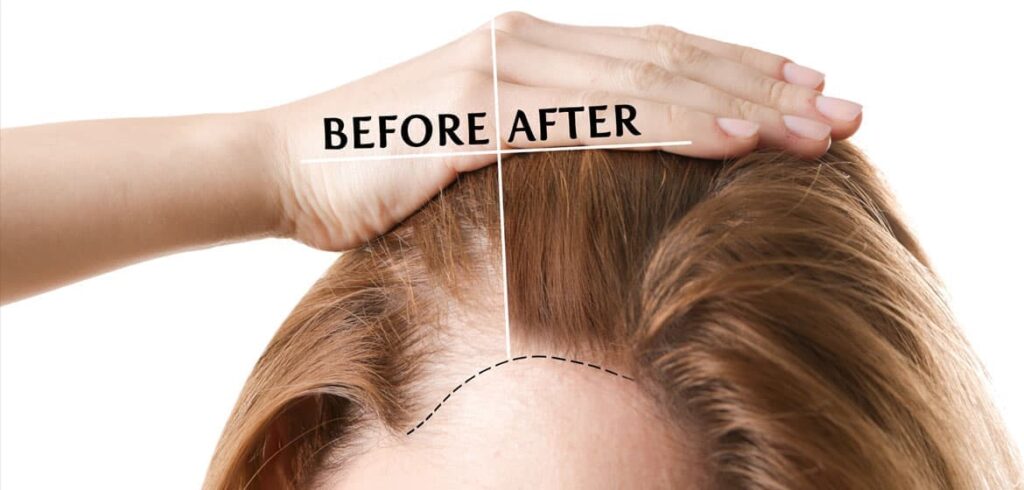

Hair transplantation can be a viable option for managing Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia (FFA), particularly in advanced cases where significant hair loss and scarring have occurred. However, several factors must be considered to determine the suitability and potential success of hair transplant procedures in individuals with FFA.
Is Hair Transplant Suitable for FFA? (Candidacy Based on Disease Activity)
The suitability of a hair transplant for FFA largely depends on the activity of the disease. It is crucial that FFA is in a stable, inactive phase before considering a transplant. Active FFA can jeopardize the success of the transplant as ongoing inflammation and immune response can lead to the rejection of the newly transplanted follicles, similar to the original hair loss. A thorough evaluation by a dermatologist or trichologist is necessary to confirm that the disease has not progressed for at least a year, indicating stability.
How Does Hair Transplant Work for FFA?
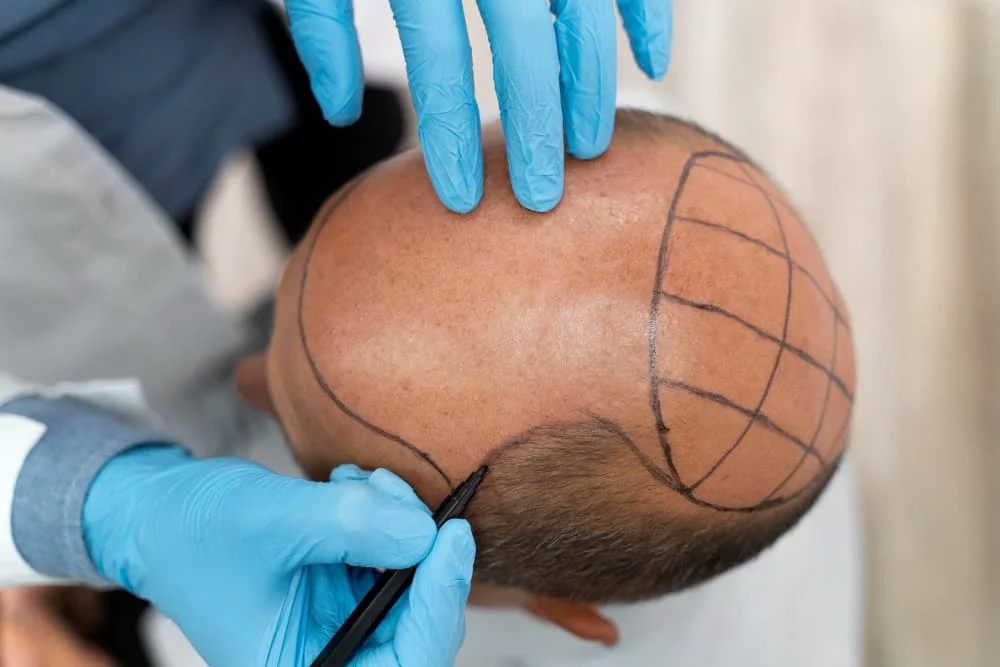
The hair transplant procedure for frontal fibrosing alopecia typically involves the extraction of hair follicles from areas of the scalp unaffected by hair loss, often the back or sides of the head where hair is usually denser and more resistant to hormonal influences. This can be done via:
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual follicles are removed one at a time, leaving minimal scarring.
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of skin with numerous hair follicles is removed, and then the follicles are individually transplanted.
The extracted follicles are then carefully implanted into the scarred, balding areas of the scalp. The procedure is delicate, requiring precise placement to ensure the best aesthetic outcome and to minimize trauma to the existing healthy hair.
Benefits & Limitations: Realistic Expectations for Hair Restoration
Benefits of hair transplantation for FFA include improved cosmetic appearance and a potentially permanent solution to hair loss if the transplanted hair takes root successfully. It can significantly enhance the patient’s self-esteem and quality of life.
However, there are limitations
- Success Rate: Not all transplanted hairs will survive the transfer, and the success can be variable based on individual factors and the skill of the surgeon.
- Disease Reactivation: There is a risk that FFA could reactivate, affecting both the original and transplanted hairs.
- Scarring: Patients must have realistic expectations regarding scarring both at the donor and recipient sites.
Setting realistic expectations is key. Patients should understand both the potential enhancements and the limits of what the procedure can achieve, especially considering the nature of frontal fibrosing alopecia . Regular follow-ups and careful monitoring after the procedure are essential to address any complications or signs of disease reactivation promptly.
Your Path to Hair Restoration in Istanbul

At Istanbul Hair Institute, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive solutions for those suffering from Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and other forms of hair loss. Our expertise and commitment to personalized care set us apart as leaders in hair restoration.
Expertise in FFA Hair Loss
Our clinic specializes in understanding and treating the unique challenges of FFA.
With a team of highly skilled professionals, we are equipped to offer the latest diagnostic and treatment techniques tailored specifically to this condition.
We understand the complexities of frontal fibrosing alopecia and ensure that our treatments align with the most current research to provide effective outcomes.

Comprehensive Approach: Diagnosis, Personalized Treatment Plans, Post-op Care

We believe in a comprehensive approach to hair restoration. Starting with a detailed diagnostic process, we use advanced techniques like scalp biopsies and trichoscopy to accurately assess and confirm the stage of frontal fibrosing alopecia . Based on these findings, we develop personalized treatment plans that may include medications to stabilize the disease and surgical options for more advanced cases.
Post-operative care is crucial, and we provide detailed guidance to ensure the best outcomes. Our follow-up care includes regular check-ups to monitor the health of the transplanted hair and the stability of FFA, ensuring any signs of reactivation are managed promptly.
Success Stories: Showcase Patient Testimonials
Our patients’ success stories are a testament to our commitment and expertise.
Many who have undergone treatment at our clinic report not only improved hair appearance but also enhanced self-confidence.
These testimonials highlight the positive impact that our specialized care has on the lives of our patients, making them a powerful affirmation of our dedication and expertise.

Free Consultation: Encourage Potential Clients to Take the First Step
If you are struggling with hair loss and think you might have FFA, we encourage you to take the first step towards recovery by scheduling a free consultation with us. This no-obligation consultation will allow you to understand your condition better, explore treatment options, and see how personalized care can make a difference in your life.
Take control of your hair health today. Contact us at Istanbul Hair Institute, and let us help you on your path to hair restoration in the heart of Istanbul.
Make Your Appointment
Recent Posts
-
 Does Creatine Cause Hair Loss? Separating Fact from Fiction21 Jan 2025
Does Creatine Cause Hair Loss? Separating Fact from Fiction21 Jan 2025 -
 How Long Does Hair Transplant Last? A Comprehensive Guide to Long-Term Results15 Jan 2025
How Long Does Hair Transplant Last? A Comprehensive Guide to Long-Term Results15 Jan 2025 -
 Hair Loss After Hair Transplantation: Is It Normal and What to Do?13 Jan 2025
Hair Loss After Hair Transplantation: Is It Normal and What to Do?13 Jan 2025 -
 Donor Area in Hair Transplant: All You Need to Know - Istanbul Hair Institute06 Jan 2025
Donor Area in Hair Transplant: All You Need to Know - Istanbul Hair Institute06 Jan 2025 -
 The Connection Between Oral Health and Overall Health03 Jan 2025
The Connection Between Oral Health and Overall Health03 Jan 2025

